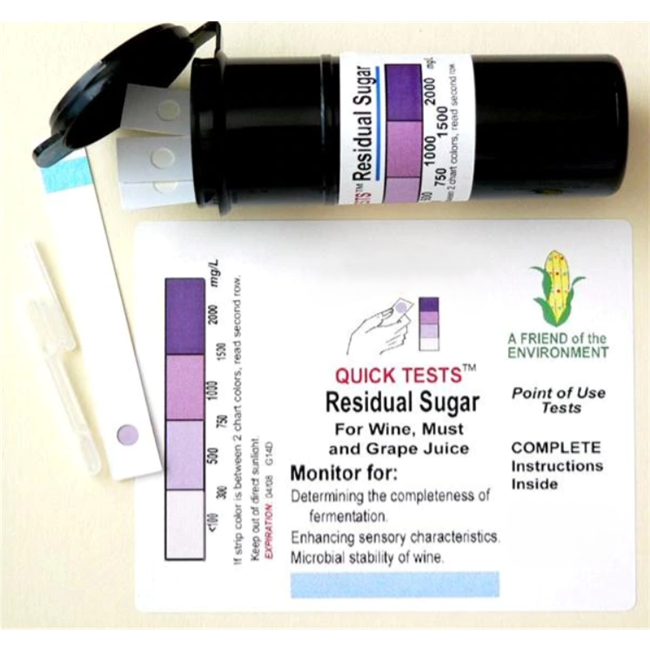
This test is intended for
measuring the levels of residual yeast-fermentable sugar in fermented must and
wine. It can also be used for testing other juices and natural fermentations.
It will not detect sucrose. Residual Sugar measures the sugars reduced in
primary fermentation. The test range is 100-2,000 mg/L.
Residual sugar is that amount
of sugar left following completion of primary (alcoholic) fermentation. The
residual sugar can vary over a wide range depending primarily on desired wine
style and secondarily on characteristics of the original must, e.g., level of
titratable acidity. Residual sugar concentrations are important for determining
the completeness of fermentation, for sensory characteristics, and for
microbial stability of wine. Technically “dry table wines with no fermentable
sugar” are typically defined as having a reducing sugar concentration of less
than 2 g/L, although in a sensory context, the absence of perceived sweetness
is achieved at concentrations below 5 g/L.
Reducing sugars in wine
consist of hexoses (mainly glucose and fructose) and pentoses (mainly arabinose
and xylose). The pentoses are not fermentable by wine yeasts. Since pentoses
alone can vary from 0.4 to 2.0 g/L,1, 2 the best measure of the completion of
primary fermentation is the determination of glucose plus fructose.
Each kit contains the number
of tests and samplers corresponding to the size of the kit.
Other Available Kit Options:
|
Part Number |
Description
|
Pricing
|
|
AC-220-20 |
Accuvin Residual Sugar 100-2,000
mg/L Test Kit (20 tests/kit) |
Call for Pricing |
|
AC-220-50 |
Accuvin Residual Sugar 100-2,000
mg/L Test Kit (50 tests/kit) |
Call for Pricing |
|
AC-220-100 |
Accuvin Residual Sugar 100-2,000
mg/L Test Kit (100 tests/kit) |
Call for Pricing |